Goal-gradient Effect
The goal-gradient effect is a psychological phenomenon that has been widely studied in fields such as psychology, economics, and marketing. However, it can also be applied to design, particularly in user experience (UX) design.
Goal-gradient effect in design
In UX design, the goal-gradient effect refers to the idea that users tend to be more motivated and engaged as they get closer to achieving a goal or completing a task. This effect can be used to create more effective designs and interfaces that encourage users to complete tasks and engage with the product.
Here are some ways that the goal-gradient effect can be applied in UX design:
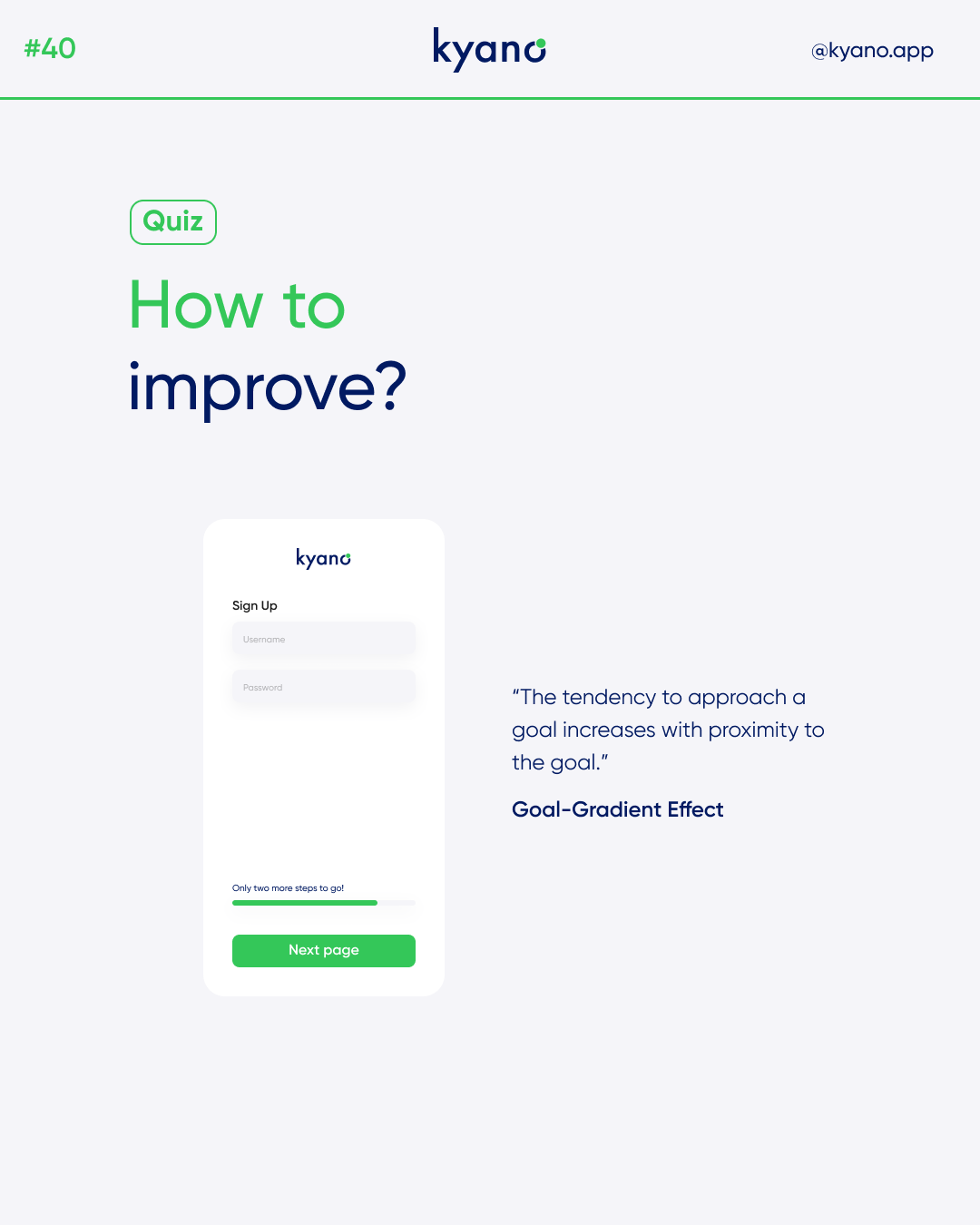
Progress bars
One way to use the goal-gradient effect is to include progress bars in your design. Progress bars visually indicate how far the user has progressed in a task or goal. As users see their progress, they are more likely to be motivated to complete the task and achieve the goal. You can use this for the password design!
Gamification
Gamification is the process of incorporating game elements into non-game contexts, such as UX design. By creating a game-like experience, users are more likely to be engaged and motivated to complete tasks. The use of rewards, badges, and leaderboards can create a sense of accomplishment and encourage users to continue using the product.
Feedback
Providing feedback to users as they complete a task can also encourage them to continue. Positive feedback, such as a “well done” message or a congratulatory animation, can create a sense of accomplishment and motivate users to continue.
Personalization
Personalizing the user experience based on their progress can also be effective. For example, showing personalized recommendations based on completed tasks or goals can motivate users to continue using the product.
In conclusion, the goal-gradient effect is a powerful tool that can be applied in UX design to encourage users to complete tasks and engage with the product.